What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that relies on the unique biological characteristics of individuals to verify they are who they say they are. Biometric authentication systems compare physical or behavioral traits to stored, confirmed, authentic data in a database. If both samples of the biometric data match, authentication is confirmed. Typically, biometric authentication is used to manage access to physical and digital resources, such as buildings, rooms and computing devices.
Biometric identification uses biometrics, such as fingerprints or retina scans, to identify a person, whereas biometric authentication is the use of biometrics to verify people are who they claim to be
Biometric authentication methods
The following technologies can be used to digitally identify people or grant them permission to access a system
- Chemical biometric devices
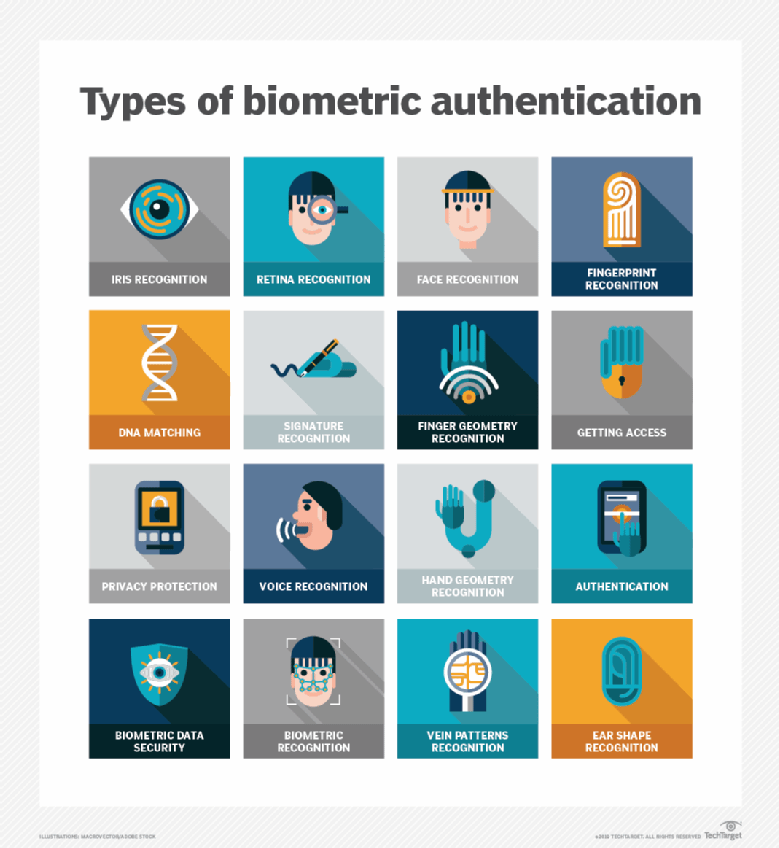
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) matching uses genetic material to identify a person.
- Visual biometric devices
- Retina scans identify subjects by analyzing the pattern of blood vessels at the back of their eyes.
- Fingerprint scanning identifies people based on their fingerprints
- Hand geometry recognition verifies identity or authorizes transactions using a mathematical representation of the unique characteristics of people’s hands. This is done by measuring the distances between various parts of the hand, including finger length, finger breadth and the shape of the valleys between the knuckles.
- Facial recognition relies on the unique characteristics and patterns of people’s faces to confirm their identity. The system identifies 80 nodal points on a human face, which make up numeric codes called faceprints.
- Ear authentication verifies identity based on users’ unique ear shape.
- Signature recognition uses pattern recognition to identify individuals based on their handwritten signature.
What are the components of biometric authentication devices?
A biometric device includes three components: a reader or scanning device, technology to convert and compare collected biometric data, and a database for storage.
A sensor is a device that measures and captures biometric data. For example, it could be a fingerprint reader, voice analyzer or retina scanner. These devices collect data to compare to the stored information for a match. The software processes the biometric data and compares it to match points in the stored data. Most biometric data is stored in a database that is tied to a central server on which all data is housed. However, another method of storing biometric data is cryptographically hashing it to allow authentication to be completed without direct access to the data.
What are the use cases of biometric authentication?
Law enforcement
Law enforcement and state and federal agencies use different kinds of biometric data for identification purposes. These include fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, voice samples and DNA.
For example, the Automated Fingerprint Identification System, or AFIS, is a database that is used to identify fingerprints. It was first used in the early 1970s as a way for police departments to automate their otherwise manual fingerprint identification process, making it quicker and more effective. In the past, a trained human examiner had to compare a fingerprint image to the prints on file. If there was a match, the examiner would double-check the two prints to verify the match. Today, AFIS can match a fingerprint against a database of millions of prints in a matter of minutes.
Travel
An electronic passport (e-passport) is the same size as a conventional passport and contains a microchip that stores the same biometric information as a conventional passport, including a digital photograph of the holder. A chip stores a digital image of the passport holder’s photo, which is linked to the owner’s name and other identifying information. The e-passport is issued electronically by a country-issuing authority, which checks the identity of the applicant through fingerprints or other biometric information and confirms the data in the chip with the information provided by the applicant before issuing the passport.
Health care
Hospitals use biometrics to more accurately track patients and prevent mix-ups, while clinics and doctors’ offices implement biometric authentication to keep their patients’ information secure. Using biometric data, hospitals can store, as well as access, a patient’s medical history. This information can be used to ensure the right patient gets the right care, whether that means faster identification in emergency situations or preventing medical errors.
Identity Verification Solutions
From eID we offer KYC (Know Your Customer), customer onboarding and digital identity solutions and services that help our customers to provide theirs a unique, simple, frictionless, high-security experience that meets the highest standards required in international regulations. AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and eIDAS (Electronic Identification, Authentication and etrust Services) regulations are remodeling the market by allowing customer acquisition processes to be reduced from weeks to seconds to, for example, open a bank account online with total security and complying with the law.
Our Video IDentification, Advanced and Qualified Electronic Signature, and Facial Biometric Authentication services are transforming the way in which companies and customers interact. Current eKYC solutions, powered by Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning allow businesses in any sector, such as banking, insurance, financial and investment services, to be digitally transformed, reduce digital customer onboarding costs and grow by offering a unique user experience.
AML | Anti-Money Laundering
- RegTech Company
- 5AMLD deadlines
- 6AMLD Regulation
- What is KYC (Know Your Customer)
- eKYC meaning
- What is Know Your Business (KYB)
Electronic Signature
- SignatureID, digital signature
- Advanced Electronic Signature
- eIDAS and electronic signature
- eSignature Contracts
- Certification Authorities
Video IDentification
- What is IDentity Verification
- 5AMLD deadlines
- Picture-based digital identification not
- VideoID vs face-to-face identification
- What is Digital Onboarding
- Digital Onboarding in banking
Video IDentification
- SmileID: Digital authentication service
- Biometric facial recognition
- Face biometrics in payment
- Facial biometrics eSignature
- Facial Biometric Access Control
